The Coming Impact of Coronavirus Economic Contraction in ASEAN Countries
Economics / Coronavirus Depression Apr 22, 2020 - 06:26 PM GMTBy: Dan_Steinbock
After the COVID-19 earthquake and a historical contraction, China is rebounding, whereas advanced economies face a depression-like plunge. The consequent tsunami is about to hit Southeast Asia.
As the total number of confirmed cases may exceed 3 million and deaths will surpass 200,000 in a matter of days, the U.S. and Europe account for more than 80% % of both. What was an epidemic in China at the turn of January and February grew into a pandemic in the 1st quarter, thanks to the belated mobilizations in Europe and the US.
As I predicted in a mid-March briefing (TMT, March 23), what is about to follow is the great coronavirus contraction. Its economic impact will be comparable to the 1930s Great Depression. With more data available today, we have a better idea what’s about to happen, despite extraordinary uncertainty.
No country in Southeast Asia will be immune to the impact.
COVID-19 impact on Southeast Asia
In the coming months, emerging and developing economies will seek to cope with the coming economic tsunami. With weaker healthcare systems, the poorest economies, particularly oil and commodity exporters, will take the heaviest hit.
In January, the confirmed cases in the emerging ASEAN economies varied from presumably none in Indonesia to more than 30 in Thailand.
After the 1st quarter, most saw the cases increase by 10, 100, even 1,000 times. And by mid-April, the largest case counts are in the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia (5,100-5,700), Thailand and Vietnam (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Cumulative confirmed cases in ASEAN-5
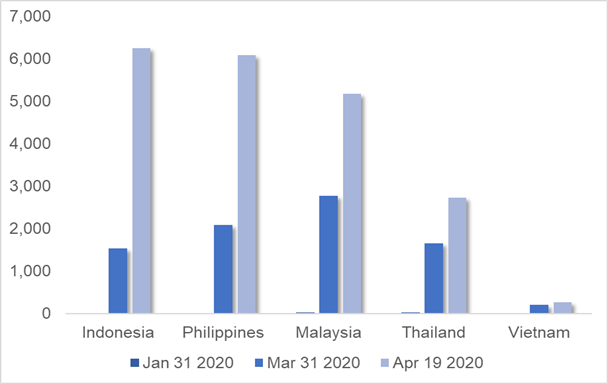
Source: WHO data, Difference Group
Size matters. The bigger the country, the greater the potential for broad COVID-19 spread. However, aggregate figures must also be seen relative to the population size (total cases/1m pop). In this view, the COVID-19 impact has been hardest in Malaysia (164), followed by the Philippines, Thailand (40-60), Indonesia and Vietnam (3-23).
To put these numbers in context, let’s recall that in Singapore (1,024) they are almost 10-fold relative to Malaysia; and in the US, twice as high as in Singapore. On the other hand, wealthier economies, such as the US and Singapore, benefit from more advanced healthcare systems.
Another caveat involves the term “confirmed” cases. The more countries test, the accurately the cases will reflect the actual impact. In this view, Malaysia, Vietnam and Thailand have used significantly more tests than the Philippines and Indonesia. Although recently the Philippine test capacity has been improving significantly.
In part, the difference is a matter of population size. The bigger the country (Indonesia, Philippines), the harder it is to test broadly. In part, it is due to the level of economic development. Upper-middle income countries (Malaysia, Thailand) tend to test more than lower-middle-income nations. Yet there are exceptions (Vietnam).
Economic impact on Southeast Asia
As the outbreak has spread, the disruption of supply chains and temporary plant shutdowns, coupled with a sudden full stop in global demand, weigh heavily on those ASEAN economies that still hope to rely mainly on export-led growth.
As Vietnam, as well as Singapore and Malaysia, have discovered, two years of trade wars and a few months of a global pandemic can undermine a decade of export recovery. In turn, those countries that depend on both tourism and exports (Vietnam, Singapore, Malaysia) must now cope with longer-term economic malaise.
In emerging economies, healthcare systems lack adequate capacity against the pandemic. If these countries had not implemented quarantines and lockdowns, they would suffer disproportionately from new virus clusters and new virus waves in the future. If they implement quarantines and lockdowns that are not adequately enforced, the net effect will be the same. And when these countries successfully execute effective quarantines, these will severely penalize their economies as domestic consumption and the businesses will take a severe hit.
So, the new baseline scenario is that Indonesia, Philippines and Vietnam will all suffer a severe growth contraction in the 2nd quarter that will cast a long shadow over the year. In Indonesia, the contraction will mean a plunge from 5.0% in 2019 to 0.5% in 2020; in the Philippines, the comparable figures are currently seen as 5.9% and 0.6%, respectively.
Better positioned initially, Vietnam’s GDP growth will fall from 7.0% to 2.7%, if it can minimize the virus impact at home. Philippines could have been better positioned against the crisis, but that advantage was largely lost with the spring 2019 budget debacle (compare my column on TMT, Jan 28, 2019).
Assuming a relatively strong rebound scenario, ASEAN economies could have a V-shaped rebound by 2021, when Indonesia and Philippines could perform better than Vietnam (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Expected coronavirus contraction in ASEAN-5
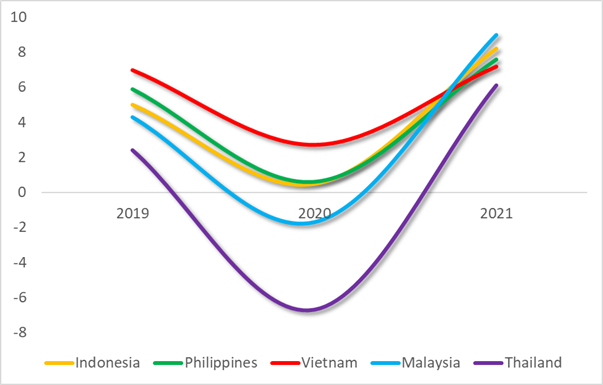
Source: IMF data, Difference Group
However, he current baseline scenario may still prove too optimistic. The challenges in the West could linger over the 3rd quarter, while the devastation in emerging and developing economies could spill over the latter half of the year, with adverse feedback effects. A new virus wave could follow in the fall. Imported infections could accelerate toward fall 2020 and spring 2021.
And as the heavily-indebted advanced economies are now taking record-volumes of new debt to support their economies, they could face new debt crises, which would spill over to poorer countries, through trade, investment, and finance. The resulting financial tightening might undermine current progress in many countries – and so on.
Should any of these scenarios materialize, the kind of strong and broad rebound that many international observers currently expect (or rather, hope) would deteriorate into a weaker and slower, longer-term process.
We can all hope for the best, but it would be very naïve not to prepare for worse.
Dr. Dan Steinbock is the founder of Difference Group and has served at the India, China and America Institute (US), Shanghai Institute for International Studies (China) and the EU Center (Singapore). For more, see http://www.differencegroup.net/
© 2020 Copyright Dan Steinbock - All Rights Reserved
Disclaimer: The above is a matter of opinion provided for general information purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Information and analysis above are derived from sources and utilising methods believed to be reliable, but we cannot accept responsibility for any losses you may incur as a result of this analysis. Individuals should consult with their personal financial advisors.
Dan Steinbock Archive |
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



