Bank Losses Spreading as Interest Rate Derivatives Start Imploding
Interest-Rates / Credit Crisis 2009 Mar 31, 2009 - 11:10 AM GMT Martin Weiss writes:For the first time in history, U.S. banks have suffered large, ominous losses in a giant sector that, until now, they thought was solid: bets on interest rates.
Martin Weiss writes:For the first time in history, U.S. banks have suffered large, ominous losses in a giant sector that, until now, they thought was solid: bets on interest rates.
In a moment, I'll explain what this means for your savings and your stocks.
But first, here's the alarming news: According to the fourth quarter report just released this past Friday by the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), commercial banks lost a record $3.4 billion in interest rate derivatives, or more than seven times their worst previous quarterly loss in that category. 1
And here's why the losses are so ominous:
Until the third quarter of last year, the banks' losses in derivatives were almost entirely confined to credit default swaps — bets on failing companies and sinking investments.
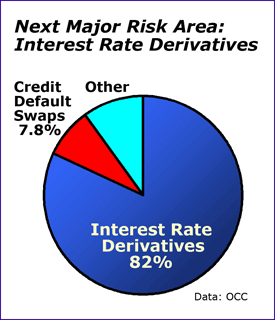 |
But credit default swaps are actually a much smaller sector, representing only 7.8 percent of the total derivatives market.
Now, with these new losses in interest rate derivatives, the disease has begun to infect a sector that encompasses a whopping 82 percent of the derivatives market. 2
Thus, considering their far larger volume, any threat to interest rate derivatives could be far more serious than anything we've seen so far.
Meanwhile, time bombs continue to explode in the credit default swaps as well, delivering another massive loss of nearly $9 billion in the fourth quarter.
And remember: These represent the aggregate total for the entire banking industry, after netting out the results of banks with profitable trading.
Why This Crisis Could Be Nearly as Bad as the Banking Crisis of 1929-31
Yes, I know the standard argument: In 1929, bank regulation and depositor protection was primarily run by state governments. Now, with the FDIC, the OCC, and more direct Federal Reserve intervention, it's far more centralized.
But offsetting that strength are serious weaknesses in the banking system that did not exist in the 1930s:
• In 1929, there were fewer giant banks. They controlled a smaller share of the total market. And they were generally stronger than the thousands of community banks around the country. Today, by contrast, the nation's high-roller megabanks dominate the market.
• In 1929, derivatives were virtually nonexistent. Not today! U.S. banks alone control $200.4 trillion; and it's precisely in this dangerous sector that the megabanks dominate the most.
According to the OCC's Q4 2008 report , America's top five commercial banks control 96 percent of the industry's total derivatives, while the top 25 control 99.78 percent. In other words, for every $100 dollar of derivatives, the big banks have $99.78 … while the rest of the nation's 7,000-plus banking institutions control a meager 22 cents! 3
This is a massively dangerous concentration of risk.
The large banks are exposed to the danger that buyers will vanish, markets will suddenly become illiquid, and they'll be unable to unload their positions without accepting wipe-out losses. Has this ever happened? Unfortunately, yes. In fact, it's the primary reason they lost a record $3.4 billion in the last three months of 2008.
The large banks are exposed to the danger that, with exploding federal deficits and new fears of inflation, interest rates will suddenly surge, delivering a whole new round of even bigger losses in the months ahead.
Worst of all, the five biggest banks are exposed to breathtaking default risk — the danger that their trading partners could fail to make good on their gambling debts, transforming even the best winning trades into some of the worst losers.
Here's our chart on these risks, updated to reflect the new data just released on Friday:
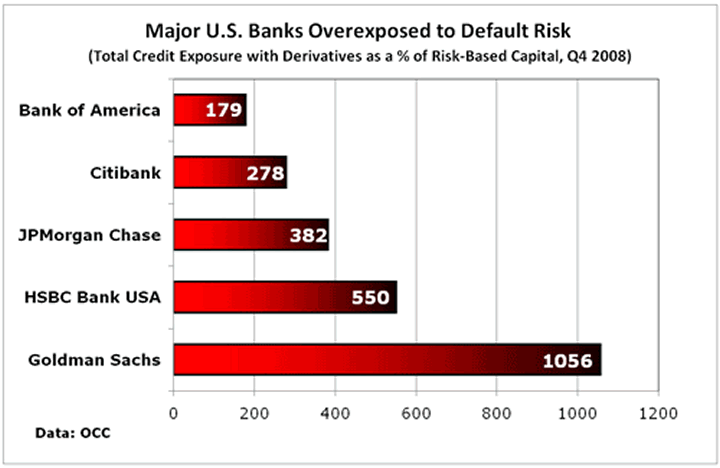
Specifically, at year-end 2008,
- Bank of America's total credit exposure to derivatives was 179 percent of its risk-based capital;
- Citibank's was 278 percent;
- JPMorgan Chase's, 382 percent; and
- HSBC America's, 550 percent. 4
What's excessive? The banking regulators won't tell us. But as a rule, exposure of more than 25 percent in any one major risk area is too much, in my view.
And if you think these four banks are overexposed, wait till you see the super-high roller that the OCC has just added to its quarterly reports: Goldman Sachs.
According to the OCC, Goldman Sachs' total credit exposure at year-end was 1,056 percent, or over ten times more than its capital.
The folks at Goldman think they're smart, and they are. They say they can handle large risks, and usually they can. But not in a sinking global economy! And not when the exposure reaches such stratospheric extremes!
Major Impact on the Stock Market
In the 1930s, the banking crisis helped drive the economy into depression and the stock market into its worst decline of the century.
The same is happening today. Whether the nation's big banks are bailed out by the federal government or not, the fact remains that they're jacking up credit standards, squeezing off credit lines, and even shutting down major segments of their lending operations.
And regardless of how much lawmakers try to arm-twist banks to lend more, it's rarely happening. With scant exceptions, bank capital has been reduced, sometimes decimated. The risk of lending has gone through the roof. And many of the more prudent borrowers don't even want bank loans to begin with.
Those credit shortages, both acute and chronic, have a big impact on the economy and the stock market. Moreover, unlike the 1930s, banks themselves are publicly traded companies whose shares make up a substantial portion of the S&P 500.
The big lesson to be learned: Don't pooh-pooh comparisons between today's bear market and the deep bear market of 1929-32.
From its peak in 1929, the Dow Jones Industrials Average fell 89 percent. Compared to the Dow's peak in 2007, that would be tantamount to a plunge of more than 12,600 points — to a low of approximately 1500, or an additional 81 percent decline from the Friday's 7776.
Even a decline of half that magnitude would still leave the Dow well below the 5000 level, which remains our current target.
Does this preclude sharp rallies? Absolutely not! From its recent March 6 bottom to last week's peak, the Dow has already jumped a resounding 21 percent in just 20 short days. And the rally may still not be over.
But this is nothing unusual. In the 1929-32 period, the Dow enjoyed even sharper rallies, and those rallies did nothing to end the great bear market. My father, who made a fortune shorting stocks in that period, explains it this way:
“In the 1930s, at each step down the slippery slope of the market's decline, Washington would periodically announce some new initiative to turn things around.
“President Hoover would give a new pep talk promising ‘prosperity around the corner.' And often, the Dow staged dramatic rallies — up 30 percent on the first round, 48 percent on the second, 23 percent on the third, and more.
“Each time, I sought to use the rallies as selling opportunities. I persuaded more of my clients to get rid of their stocks and pile up cash. I even told them to take their money out of shaky banks.”
Your approach today should be similar. Specifically,
Step 1. Keep as much as 90 percent of your money SAFE, as follows:
- For your banking needs, seek to use only institutions with a Financial Strength Rating of B+ or better. For a list, click here . Then, in the index, scroll down to item 13, “Strongest Banks and Thrifts in the U.S.”
- Make sure your deposits remain comfortably under the old FDIC insurance coverage limits of $100,000. The new $250,000 per account limit is temporary and, in my view, not something to rely on long term.
- Move the bulk of your money to Treasury bills or equivalent. You can buy them (a) directly from the U.S. Treasury Department by opening an account at TreasuryDirect , (b) through your broker, or (c) via a Treasury-only money market fund. For further instructions, and review sections 1 through 3 — “How to Buy Treasury Bills or Equivalent,” “How to Use Your Treasury-Only Money Fund as a Bank,” and “How to Set Up a Single, Safe Account for Nearly All Your Savings and Checking.”
Important: You may have seen some commentary from experts that “Treasuries are not safe.” But when you review their comments more carefully, you'll probably see they're not referring to Treasury bills, which have virtually zero price risk. They're talking strictly about Treasury notes or bonds, which can — and probably will — suffer serious declines in their market value.
Step 2. If you missed the opportunity to greatly reduce your exposure to the stock market in 2007 or 2008, you now have another chance. And the more the market rises from here, the more you should sell.
Step 3. If you are still exposed to stock market declines, seriously consider inverse ETFs, ideal for helping you hedge against that risk. (For more background information, see my 2007 report, How to Protect Your Stock Portfolio From the Spreading Credit Crunch .)
Step 4. If you have funds you can afford to risk, seriously consider two major profit opportunities in the months ahead:
- To profit handsomely from the market's next decline. The best time to start: When Wall Street pundits begin declaring “the bear is dead.” They'll be wrong. But their enthusiasm can be one of the telltale signs that the latest rally is probably ending.
- To profit even more when the market hits rock bottom and you can buy some of the nation's best companies for pennies on the dollar. The ideal time to buy: When Wall Street is convinced the world is virtually “coming to an end.” They will be wrong, again. But that kind of extreme pessimism could be one of your signals that a real recovery is about to begin.
Good luck and God bless!
Martin
This investment news is brought to you by Money and Markets . Money and Markets is a free daily investment newsletter from Martin D. Weiss and Weiss Research analysts offering the latest investing news and financial insights for the stock market, including tips and advice on investing in gold, energy and oil. Dr. Weiss is a leader in the fields of investing, interest rates, financial safety and economic forecasting. To view archives or subscribe, visit http://www.moneyandmarkets.com .
Money and Markets Archive |
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



